Monitoring from a stationary position
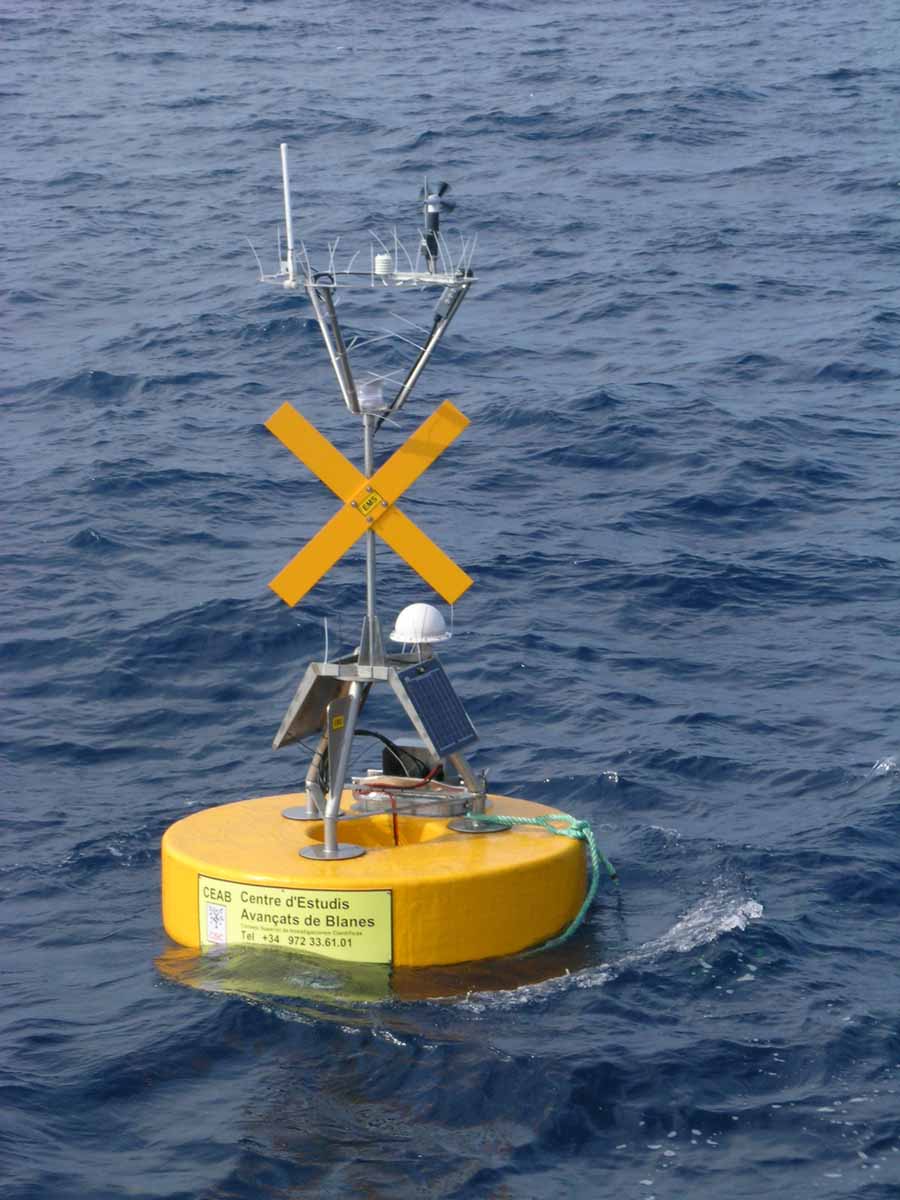

Oceanographic buoy / Boya oceanográfica
|
| |
The meteorological and oceanographic buoy has a toroid-shaped surface buoy, also called "Donut", holding various oceanographic and meteorological instruments along with a GSM (modem) for telemetry, data logger for data storage, GPS, and batteries charged by a set of photovoltaic panels through a charge controller.
Connections among the system components are done with neoprene rubber and polyurethane-jacketed cables and Sub Conn connectors.
The toroid-shaped buoy is helpful for holding instrumentation submerged near the surface, thus providing reliable measurements from shallower water layers.
Main features
- Active and passive signaling in accordance with regulations in force (Cruz de San Andrés, night flash, radar reflector, body painted yellow and indications of the property).
- Minimum buoyancy of 200 kg.
- Dimensions of Ø 2000 x 500 mm.
- Mast height of 2000 mm above sea level.
- Flotation Material: Dense polystyrene covered with fiberglass, 10 mm thick and high resistance.
- Structures and substructures are of stainless steel 316L.
- Zinc anodes for cathode protection to avoid salt-water corrosion, are interchangeable
- Waterproof room for storing batteries, data logger and additional electrical devices
- Ballast weight for keeping the buoy structure upright
- GPS
- Rechargeable battery and photovoltaic panels
- Data acquisition system (data logger)
- Telemetry system (GSM/GPRS)
Oceanographic instruments
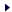 One SBE37 Microcat CT measures surface water temperature and salinity. One SBE37 Microcat CT measures surface water temperature and salinity.
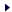 Two SBE 16 plus IM inductively coupled to the mooring cable at 25 and 50 m depth equipped with the following sensors: Two SBE 16 plus IM inductively coupled to the mooring cable at 25 and 50 m depth equipped with the following sensors:
-
Temperature
-
Salinity
-
Dissolved Oxygen
-
Irradiance (PAR)
-
Turbidity
-
Chlorophyll fluorescence
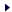 One Workhorse Monitor ADCP (Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler) that converts the backscattered sound into components of water current velocity in the upper 120 m water layer. One Workhorse Monitor ADCP (Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler) that converts the backscattered sound into components of water current velocity in the upper 120 m water layer.
Meteorological instruments
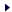 A meteorological station consisting of a number of instruments to measure: A meteorological station consisting of a number of instruments to measure:

|


